Effi cacy of classes of interventions Classes of interventions are
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Last updated 07 juillet 2024

Download scientific diagram | Effi cacy of classes of interventions Classes of interventions are ordered according to effi cacy ranking from largest mean eff ect (top, left) to smallest mean eff ect (bottom, right). Data in blue represent the eff ects on symptoms of social anxiety (SMD [95% CrI]); SMD less than 0 favours the intervention in the row. Data in green represent the eff ects on recovery (RR [95% CrI]); RR greater than 1 favours the intervention in the column. Signifi cant results are shaded dark blue and dark green. CBT=cognitive-behavioural therapy. CrI=credible interval. EXER=promotion of exercise. EXPO=exposure and social skills. MAOI=monoamine oxidase inhibitors. NSSA=noradrenergic and specifi c serotonergic antidepressants. OTHER=other psychological therapy. PDPT=psychodynamic psychotherapy. PSYP=psychological placebo. RR=risk ratio. SHNS=self-help without support. SHWS=self-help with support. SMD=standardised mean diff erence. SNRI=serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. SSRI=selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor. from publication: Psychological and pharmacological interventions for social anxiety disorder in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis | Background Social anxiety disorder—a chronic and naturally unremitting disease that causes substantial impairment—can be treated with pharmacological, psychological, and self-help interventions. We aimed to compare these interventions and to identify which are most effective | Social Phobia, Network Meta-Analysis and Psychology | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Type and effectiveness of community-based interventions in improving knowledge related to cardiovascular diseases and risk factors: A systematic review - ScienceDirect

Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness against malaria of three types of dual-active-ingredient long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) compared with pyrethroid-only LLINs in Tanzania: a four-arm, cluster-randomised trial - The Lancet
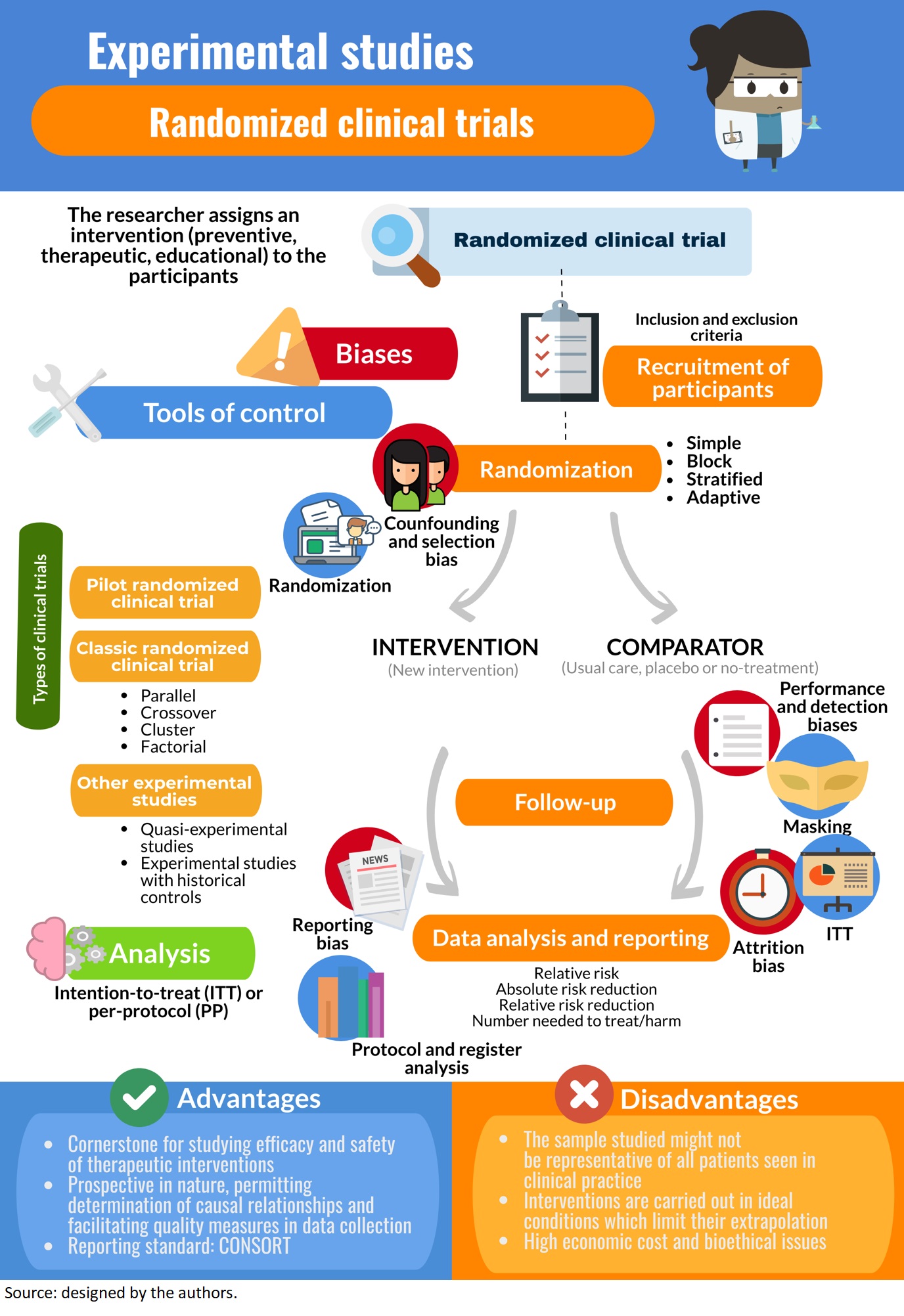
General concepts in biostatistics and clinical epidemiology: Experimental studies with randomized clinical trial design - Medwave
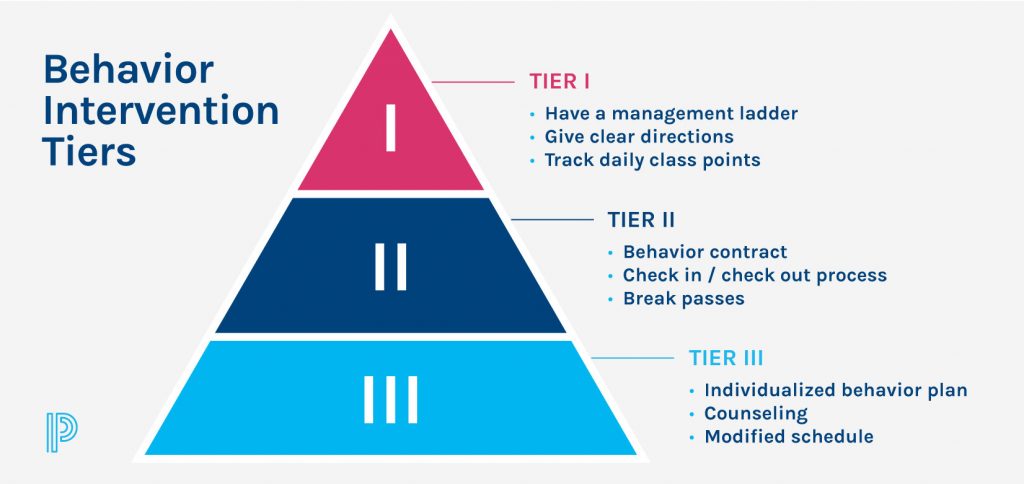
What Is the Difference Between Tier 1, 2, and 3 Behavior Interventions?

Crowdsourcing interventions to promote uptake of COVID-19 booster vaccines - eClinicalMedicine
ClassWide Peer Tutoring: An Effective Strategy for Students With Emotional and Behavioral Disorders - Lisa Bowman-Perrott, 2009
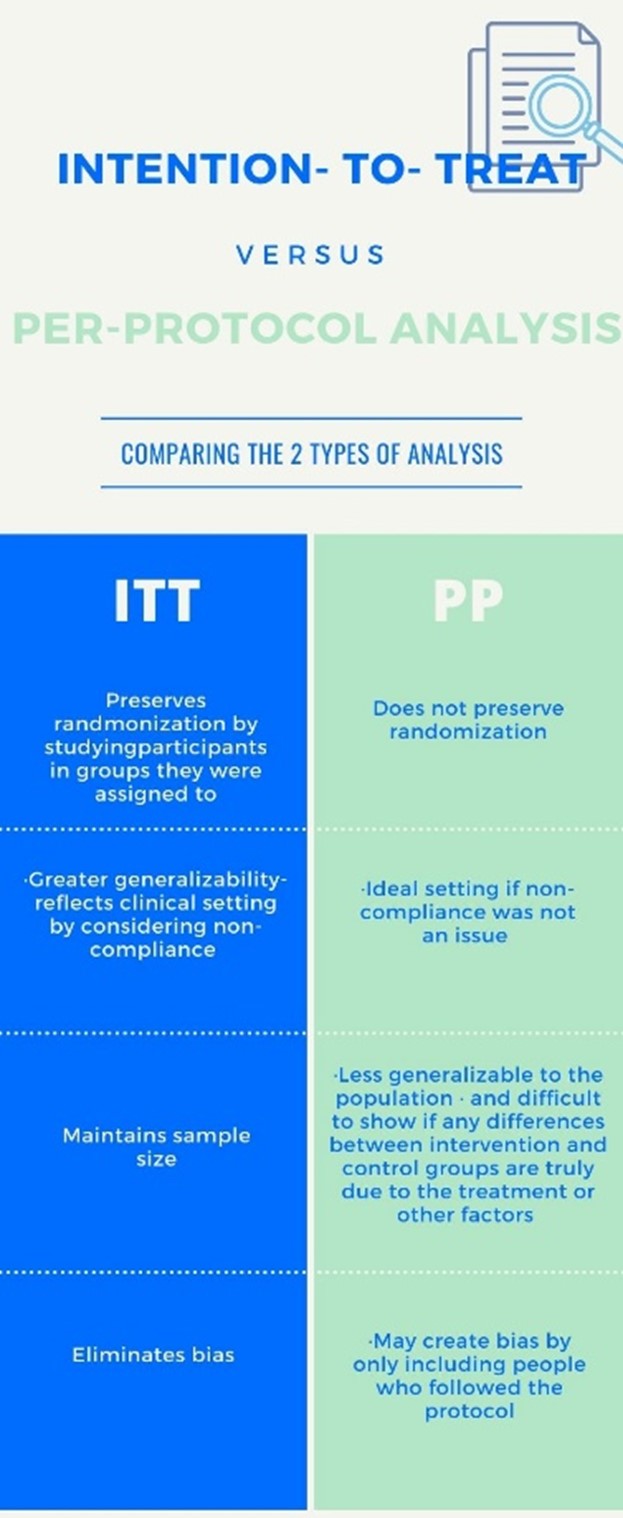
What's behind the data? ITT vs PP analysis, explained

Efficacy of the Responsive Classroom Approach: Results From a 3-Year, Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Trial - Sara E. Rimm-Kaufman, Ross A. A. Larsen, Alison E. Baroody, Timothy W. Curby, Michelle Ko, Julia B.
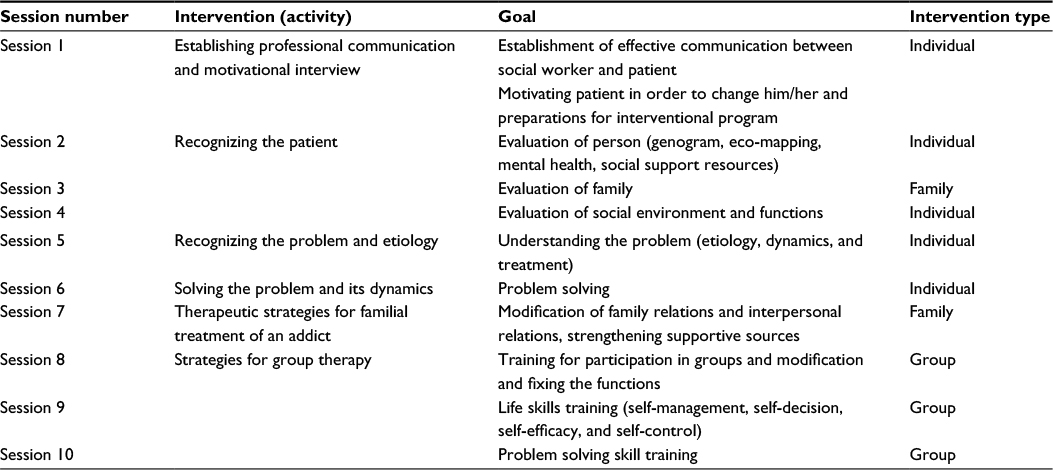
Effectiveness of social work intervention with a systematic approach t

Self‐efficacy and healthcare costs in patients with chronic heart failure or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - Blanck - ESC Heart Failure - Wiley Online Library
Recommandé pour vous
 Retour Pedal Support Spring, 77 01 208 109 Operation14 Jul 2023
Retour Pedal Support Spring, 77 01 208 109 Operation14 Jul 2023 1pc 4658700QAB 77 01 208 109 7701208109 Clutch Pedal Return Spring14 Jul 2023
1pc 4658700QAB 77 01 208 109 7701208109 Clutch Pedal Return Spring14 Jul 2023 RetourPedal Assist Spring,Pedal Support Spring 77 01 208 109 Support Spring Replacement for Vauxhall Vivaro A 2002 to 201514 Jul 2023
RetourPedal Assist Spring,Pedal Support Spring 77 01 208 109 Support Spring Replacement for Vauxhall Vivaro A 2002 to 201514 Jul 2023 Kit de réparation 77 01 208 109 7701208109 Abs Embrayage Pédale14 Jul 2023
Kit de réparation 77 01 208 109 7701208109 Abs Embrayage Pédale14 Jul 2023- Spring pedal clutch trafic ii vivaro i and oe14 Jul 2023
 Repair Kit 1pc 4658700QAB 77 01 208 109 Clutch Pedal Return Spring14 Jul 2023
Repair Kit 1pc 4658700QAB 77 01 208 109 Clutch Pedal Return Spring14 Jul 2023 Peugeot 208 1.2 puretech 82cv Active - Voitures14 Jul 2023
Peugeot 208 1.2 puretech 82cv Active - Voitures14 Jul 2023 Ressort D'assistance De Pédale D'embrayage 77 01 208 109 Pour14 Jul 2023
Ressort D'assistance De Pédale D'embrayage 77 01 208 109 Pour14 Jul 2023- Nintendo leaks continue, this time featuring N64 development14 Jul 2023
 BUTTON-LOCK, SL: Nissan / Renault 825646R -compatibility14 Jul 2023
BUTTON-LOCK, SL: Nissan / Renault 825646R -compatibility14 Jul 2023
Tu pourrais aussi aimer
 LEDGlow Build Your Own Advanced Million Color LED Motorcycle Lighting Kit14 Jul 2023
LEDGlow Build Your Own Advanced Million Color LED Motorcycle Lighting Kit14 Jul 2023 How to Make Magret de Canard - A Hedgehog in the Kitchen14 Jul 2023
How to Make Magret de Canard - A Hedgehog in the Kitchen14 Jul 2023 Sunnecko Ciseaux Cuisine en Acier Inoxydable, Ciseau Cuisine14 Jul 2023
Sunnecko Ciseaux Cuisine en Acier Inoxydable, Ciseau Cuisine14 Jul 2023 Wenko Vacuum-Loc Háček chrom, 2 ks koupit v OBI14 Jul 2023
Wenko Vacuum-Loc Háček chrom, 2 ks koupit v OBI14 Jul 2023 Canard de pêche Dam Sprl : King Jouet, Activités d'éveil Dam Sprl14 Jul 2023
Canard de pêche Dam Sprl : King Jouet, Activités d'éveil Dam Sprl14 Jul 2023 Candide - Tapis D'éveil, Tapis De Motricité, Tapis Bébé, Multifonction 3 en 1, Couchage D'appoint, Pouf Bébé, Déhoussable, Fabriqué En France14 Jul 2023
Candide - Tapis D'éveil, Tapis De Motricité, Tapis Bébé, Multifonction 3 en 1, Couchage D'appoint, Pouf Bébé, Déhoussable, Fabriqué En France14 Jul 2023 Bonnet chaud rose fleuris femme - Maloja - GIRLS UP14 Jul 2023
Bonnet chaud rose fleuris femme - Maloja - GIRLS UP14 Jul 2023 Bandeau Bébé Fille Bandeaux Nouveau-Né Enfant en Bas Âge Bandeaux et Arcs Accessoires Cheveux Enfant 10 PCS14 Jul 2023
Bandeau Bébé Fille Bandeaux Nouveau-Né Enfant en Bas Âge Bandeaux et Arcs Accessoires Cheveux Enfant 10 PCS14 Jul 2023 CityComfort Jogging Enfant Fille - Ensemble de Survêtement Fille 414 Jul 2023
CityComfort Jogging Enfant Fille - Ensemble de Survêtement Fille 414 Jul 2023 Hot Wheels Monster Trucks Coffret de 8 véhicules aux roues géantes, jouet de voiture pour enfant, emballage durable, HGX2114 Jul 2023
Hot Wheels Monster Trucks Coffret de 8 véhicules aux roues géantes, jouet de voiture pour enfant, emballage durable, HGX2114 Jul 2023