Determining the Role of Maternally-Expressed Genes in Early Development with Maternal Crispants
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Last updated 06 juillet 2024

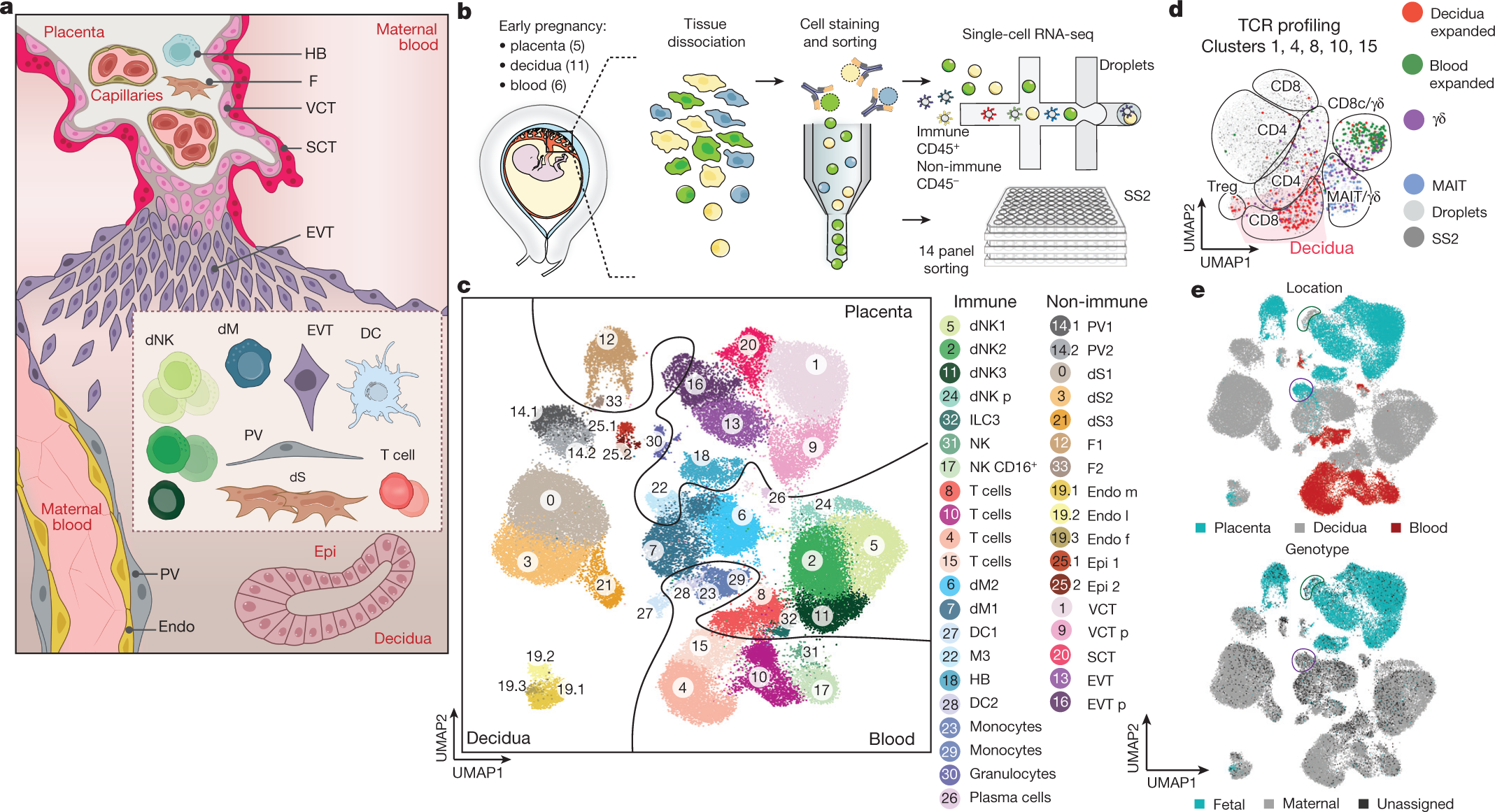
Single-cell reconstruction of the early maternal–fetal interface in humans

Early zebrafish development: it's in the maternal genes.

Loss of Fgf-responsive Pea3 transcription factors results in ciliopathy-associated phenotypes during early zebrafish development

Gene Expression Changes During Human Early Embryo Development: New Applications for Embryo Selection

Maternal immune activation alters placental histone-3 lysine-9 tri-methylation, offspring sensorimotor processing, and hypothalamic transposable element expression in a sex-specific manner - ScienceDirect

All Protocols and Video Articles in JoVE
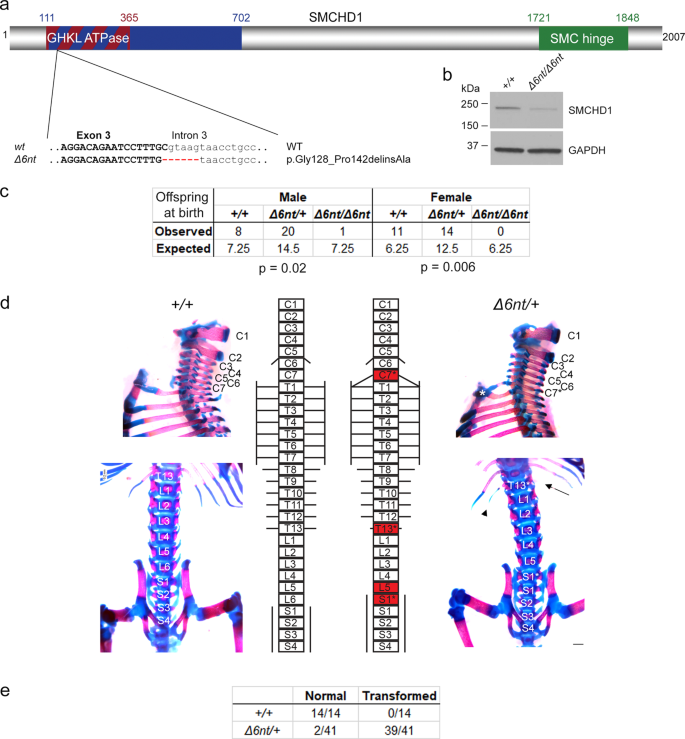
HOX epimutations driven by maternal SMCHD1/LRIF1 haploinsufficiency trigger homeotic transformations in genetically wildtype offspring

JCI - Take your mother's ferry: preimplantation embryo development requires maternal karyopherins for nuclear transport

HOX epimutations driven by maternal SMCHD1/LRIF1 haploinsufficiency trigger homeotic transformations in genetically wildtype offspring
Placental imprinting: Emerging mechanisms and functions

Axis induction defects in embryos from mothers homozygous for three
Recommandé pour vous
 L'effet maternel14 Jul 2023
L'effet maternel14 Jul 2023 Gène zygotique : définition et explications14 Jul 2023
Gène zygotique : définition et explications14 Jul 2023 L'effet maternel, Linhart, Virginie14 Jul 2023
L'effet maternel, Linhart, Virginie14 Jul 2023 Virginie Linhart (auteur de L'effet maternel) - Babelio14 Jul 2023
Virginie Linhart (auteur de L'effet maternel) - Babelio14 Jul 2023![PDF] Quand la mère est plus que responsable du devenir de sa progéniture : les mutations à effet maternel](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8eb3373d1827ee27bf81337a745893f8faca5ebd/5-Figure3-1.png) PDF] Quand la mère est plus que responsable du devenir de sa progéniture : les mutations à effet maternel14 Jul 2023
PDF] Quand la mère est plus que responsable du devenir de sa progéniture : les mutations à effet maternel14 Jul 2023 Histoire d'une question anatomique - La répétition des parties et la construction du “paradigme” des gènes du développement - Publications scientifiques du Muséum14 Jul 2023
Histoire d'une question anatomique - La répétition des parties et la construction du “paradigme” des gènes du développement - Publications scientifiques du Muséum14 Jul 2023 Le Coin des Mots – Page 2 – Mes lectures et mes petits avis.14 Jul 2023
Le Coin des Mots – Page 2 – Mes lectures et mes petits avis.14 Jul 2023 L'effet maternel - Linhart, Virginie - Livres14 Jul 2023
L'effet maternel - Linhart, Virginie - Livres14 Jul 2023 Romans : 6 poches renversants14 Jul 2023
Romans : 6 poches renversants14 Jul 2023- La Leche League Belgique - Une étude dévoile l'effet bénéfique longue durée de l'allaitement maternel sur la digestion de l'enfant qui a été allaité. En effet, l'allaitement pendant au moins 7 mois14 Jul 2023
Tu pourrais aussi aimer
 Cadre transparent 4 empreintes - Family Touch - Kits Empreintes14 Jul 2023
Cadre transparent 4 empreintes - Family Touch - Kits Empreintes14 Jul 2023 Matelas Mousse 90x190 cm CONFOBED MIA - Conforama14 Jul 2023
Matelas Mousse 90x190 cm CONFOBED MIA - Conforama14 Jul 2023 Kenond Automatic Bird Feeder, No-Mess Bird Cage Finch Foraging14 Jul 2023
Kenond Automatic Bird Feeder, No-Mess Bird Cage Finch Foraging14 Jul 2023 3 paires de chaussettes sport courtes blanches Umbro taille 43/4614 Jul 2023
3 paires de chaussettes sport courtes blanches Umbro taille 43/4614 Jul 2023 Les Immanquables Diverto cette semaine : La petite fille sous la14 Jul 2023
Les Immanquables Diverto cette semaine : La petite fille sous la14 Jul 2023 HYGIENE ET SOINS SPORTIFS Skip SENSITIVE - Lessive 26 capsules x414 Jul 2023
HYGIENE ET SOINS SPORTIFS Skip SENSITIVE - Lessive 26 capsules x414 Jul 2023 Mille Borne - Accessibility Kit (1000 miles) – 64 Ounce Games14 Jul 2023
Mille Borne - Accessibility Kit (1000 miles) – 64 Ounce Games14 Jul 2023![Tue Mouche Electrique Interieur UV 18W Lampe Anti Moustique Destructeur d'insectes Piege a Moustique Tueur Lampe Attrape [149]](https://www.cdiscount.com/pdt2/6/3/2/2/700x700/auc3755698527632/rw/tue-mouche-electrique-interieur-uv-18w-lampe-anti.jpg) Tue Mouche Electrique Interieur UV 18W Lampe Anti Moustique Destructeur d'insectes Piege a Moustique Tueur Lampe Attrape [149]14 Jul 2023
Tue Mouche Electrique Interieur UV 18W Lampe Anti Moustique Destructeur d'insectes Piege a Moustique Tueur Lampe Attrape [149]14 Jul 2023 Future maman14 Jul 2023
Future maman14 Jul 2023 Barboteuse rouge bleu bébé garçon - yelaa14 Jul 2023
Barboteuse rouge bleu bébé garçon - yelaa14 Jul 2023
